Biosphere reserves are areas of terrestrial and coastal or marine ecosystems or its amalgamation. The biosphere reserve network was launched in 1971 by UNESCO, two years after the initiation of MAB- Man and the biosphere program. The Government of India established 18 biospheres in the country (categories generally relating to IUCN Category V Protected areas).
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
The first biosphere reserve of the world was established in 1979. According to UNESCO, as of July 2021, there are 714 Biosphere reserves across 129 countries in the world which also include 21 transboundary sites.
Latest Context:
Odisha Government has proposed to give the status of Biosphere Reserve to Mahendragiri Hill Complex. If added, it will be Odisha’s second Biosphere Reserve after Simlipal Biosphere Reserve.
The List of Biosphere Reserves in India and questions based on the same are important for candidates preparing for the IAS Exam. Aspirants looking forward to applying for UPSC CSE can visit the linked article.
This article will talk about the 11 biosphere reserves of India that are now considered as UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserve, important from the UPSC exam perspective. Also, the list of 18 Biosphere Reserves in India has been given further below in the article.
Distribution of the Biosphere Reserves across the World are as follows:
- 85 sites in 31 countries in Africa
- 33 sites in 12 countries in the Arab States
- 157 sites in 24 countries in Asia and the Pacific
- 302 sites in 38 countries in Europe and North America
- 130 sites in 21 countries in Latin America and the Caribbean.
Functions of a Biosphere Reserve
Each biosphere reserve is supposed to fulfill three harmonizing functions:
- Conservation function: to conserve genetic resources, species, ecosystems, and landscapes
- Development function: to promote sustainable human and economic development.
- Logistic support function: to provide support for research and analysing the issues of conservation and sustainable development.
Three zones of the Biosphere
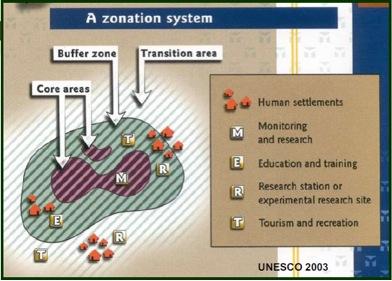
Biosphere reserves have three unified zones that aim to fulfill three harmonizing and mutually reinforcing functions:
- The core area: It involves an entirely secured and protected ecosystem that contributes to the preservation of landscapes, ecosystems, species and genetic variation.
- The buffer zone: It encompasses or adjoins the core areas. It is utilized for activities compatible with sound ecological practices that can fortify scientific research, monitoring, training, and education.
- The transition area: It is the part of the reserve where the greatest activity is permitted to promote economic and human development that is sustainable.
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
Biosphere reserves are announced by the state or central governments by notification. The Governments can nominate them under the UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme after its establishment as a biosphere reserve. There are 18 biosphere reserves in India.
| No. | Name of Biosphere Reserve | Year of Notification | Location (States) |
| 1 | Nilgiri | 1986 | Part of Wayanad, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Madumalai, Nilambur, Silent Valley, and Siruvani hills (Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka). |
| 2 | Nanda Devi | 1988 | Part of Chamoli, Pithoragarh, and Bageshwar districts (Uttarakhand). |
| 3 | Nokrek | 1988 | Part of Garo Hills (Meghalaya). |
| 4 | Great Nicobar | 1989 | Southernmost islands of Andaman And Nicobar (A&N Islands). |
| 5 | Gulf of Mannar | 1989 | The Indian part of the Gulf of Mannar between India and Sri Lanka (Tamil Nadu). |
| 6 | Manas | 1989 | Part of Kokrajhar, Bongaigaon, Barpeta, Nalbari, Kamprup, and Darang districts (Assam). |
| 7 | Sunderbans | 1989 | Part of the delta of Ganges and Brahmaputra river system
(West Bengal). |
| 8 | Simlipal | 1994 | Part of the Mayurbhanj district (Orissa). |
| 9 | Dibru-Saikhowa | 1997 | Part of Dibrugarh and Tinsukia Districts (Assam). |
| 10 | Dehang-Dibang | 1998 | Part of Siang and Dibang Valley in Arunachal Pradesh. |
| 11 | Pachmarhi | 1999 | Parts of Betul, Hoshangabad, and Chindwara districts of Madhya Pradesh. |
| 12 | Khangchendzonga | 2000 | Parts of Khangchendzonga hills and Sikkim. |
| 13 | Agasthyamalai | 2001 | Neyyar, Peppara, and Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuaries and their adjoining areas in Kerala. |
| 14 | Achanakamar – Amarkantak | 2005 | Covers parts of Anupur and Dindori districts of M.P. and parts of Bilaspur districts of Chhattishgarh State. |
| 15 | Kachchh | 2008 | Part of Kachchh, Rajkot, Surendra Nagar, and Patan Civil Districts of Gujarat State. |
| 16 | Cold Desert | 2009 | Pin Valley National Park and surroundings; Chandratal and Sarchu & Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary in Himachal Pradesh. |
| 17 | Seshachalam Hills | 2010 | Seshachalam Hill Ranges covering parts of Chittoor and Kadapa districts of Andhra Pradesh. |
| 18 | Panna | 2011 | Part of Panna and Chhattarpur districts in Madhya Pradesh. |
UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserves – International Status
Recently, Panna Biosphere Reserve was also given the International status of UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserve. The status was given in the year 2020, and prior to that, the Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve from India was also included in this list in 2018.
With the addition of the two Biosphere Reserves, 12 of the 18 biosphere reserves in the country have become part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves which is based on the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme list.
The UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserves list in India are given below:
| YEAR | NAME | STATES |
| 2000 | Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 2001 | Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 2001 | Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve | West Bengal |
| 2004 | Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | Uttarakhand |
| 2009 | Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
| 2009 | Nokrek Biosphere Reserve | Meghalaya |
| 2009 | Simlipal Biosphere Reserve | Odisha |
| 2012 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | Chhattisgarh |
| 2013 | Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | Great Nicobar |
| 2016 | Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve | Kerala and Tamil Nadu |
| 2018 | Kanchenjunga Biosphere Reserve | Part of North and West Sikkim districts |
| 2020 | Panna Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) covers globally chosen protected areas. It consists of a vibrant and interactive network of sites of distinction. It promotes the harmonious assimilation of people and nature for sustainable development in different ways. If one country declares one area as a biosphere reserve, it can nominate the same to under the UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme. If UNESCO accepts the proposal of the government, the biosphere reserve will enter into the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
Biosphere reserves in India is an important static GK topic. For information on various static GK topics, check the article linked here.
Biosphere Conservation
UNESCO is promoting the peaceful integration of man and nature for sustainable development through participatory dialogue, awareness on poverty reduction and human well-being improvement, respect for cultural values, and society’s ability to cope with change.
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the largest and the smallest Biosphere Reserve in India?
The largest Biosphere reserve in India is the Gulf of Kachchh, Gujarat and the smallest Biosphere Reserve in India is Dibru-Saikhowa in Assam.
Which is the 1st Biosphere reserve in India?
The first Biosphere Reserve in India is the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve that is a part of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala.
Who declares the Biosphere reserve in India?
The Biosphere Reserves in India are declared by the State or Central Government through Nomination under the UNESCO’S Man & Biosphere (MAB) Programme.
What is the difference between a National Park and a Biosphere Reserve?
A national park is a reserved area of land owned by the government which is protected from industrialization, human exploitation, and pollution. Whereas, A biosphere reserve is a term given to an area for the conservation of the resources of the biosphere and the improvement of the relationship between man and the environment. For more details regarding the Difference between National Park, Biosphere Reserve and Wildlife Sanctuary aspirants can visit the linked article.
What is the Man and Biosphere Programme?
The Man and Biosphere Programme (MAB) was launched by UNESCO in 1971 to establish a scientific basis for the improvement of relationships between people and their environments.
What is the World Network of Biosphere Reserves?
The World Network of Biosphere Reserves of the MAB Programme consists of a dynamic and interactive network of sites of excellence to contribute to the 2030 Agenda and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). It promotes North-South and South-South collaboration and represents a unique tool for international co-operation through sharing knowledge, exchanging experiences, building capacity and promoting best practices



No comments:
Post a Comment